Costs and prices of AC electric motors
Comparing the price dynamics of electric motors with their estimated costs through a should cost
Published by Redazione PricePedia. .
Electrical Appliances Should CostOver the past 4 years, prices for alternating current electric motors have increased on average by 50%, as much as they had increased in the previous 15 years. In the face of this strong increase, it may be useful to verify whether it is justified or not by the variation in the production costs of an electric motor. To do this, we used the should-cost tool.
Electric Motors
In 2023, the global trade of electric motors was $64 billion. Small power motors (below 37.5 W) represent a quarter of global trade. Most of these motors are direct current. Medium power motors (with a power between 37.5W and 750W) represent the largest share of global trade, exceeding 50%. Within
medium power motors, direct current and alternating current motors almost evenly split the global demand. High-power motors (over 750W) represent the remaining 20% of global trade and are dominated by alternating current motors. This segment has been growing rapidly for several years, supported by
the exchange of motors for electric cars.
The analysis contained in this article focuses on alternating current motors, which represent half of medium power motors and the majority of high-power motors.
Construction of the Should Cost of an Alternating Current Electric Motor
Here below you can find the construction of the should-cost for an electric motor with a steel housing.
Cost Breakdown Analysis
The main materials that make up this type of electric motor are listed in the following table:
Table 1: Cost breakdown of material costs for an electric motor with a steel housing
| Material | Weight in kg per 1 kg of electric motor | Cost driver | Cost driver price January 2022 (Euro/kg) | Material cost January 2022 (Euro/kg) | % cost on total material costs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 0.40 | Copper wires (section > 6 mm) | 8.84 | 3.54 | 82.7 |
| Magnetic laminations | 0.35 | N.G.O. magnetic laminations (width ≥ 600 mm) | 1.34 | 0.47 | 11.0 |
| Steel sheet | 0.25 | Cold-rolled coils (thickness 1-3 mm) | 1.09 | 0.27 | 6.3 |
| Total | 1.00 | 4.28 | 100.0 |
The above table accounts only for the material costs required for the production of an electric motor. To calculate its total cost, material costs must be added to the costs of energy, plants, services, direct labor, and profit margins. This information can be derived from input-output matrix data
published by the central statistical institutes of various European countries. These matrices, for each macro productive sector, report the incidence of macro cost items.
In the European electrical equipment industry, the incidence of material costs on total costs averages 50%. The incidence of energy prices is on average contained. In January 2022, the base month for calculating the should cost, the incidence of energy costs in the electrical equipment industry
can be estimated at around 1%. It follows that the incidence of other costs (labor, services, etc.) can be quantified at 49% of total costs.
In the table below, the percentages of the different costs used for the calculation of the should cost of an electric motor are reported.
Table 2: Cost breakdown of an electric motor with a steel housing
| Material | Cost incidence (%) | Cost driver |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | 41.3 | Copper wires (section > 6 mm) |
| Magnetic laminations | 5.5 | N.G.O. magnetic laminations (width ≥ 600 mm) |
| Steel sheet | 3.2 | Cold-rolled coils (thickness 1-3 mm) |
| Energy | 1.0 | Total Energy Index (Europe) |
| Services and labor | 49.0 | Euro Area Consumer Price Index |
| Total | 100.0 |
The consumer price index of the Euro area was used as the cost driver for costs other than materials and energy. Although with different timing, it is reasonable to assume that these costs tend over time to align with inflation.
Should Cost
The dynamics of the should-cost related to the considered electric motor are shown in the following graph.
Graph 1: Should cost of an electric motor with a steel housing

From the analysis of this graph, the different cost levels that have characterized electric motors throughout this century are clearly evident. The second decade (from 2010 to 2020) was characterized by a substantially stable cost level. In the biennium 2021-2022, this level increased significantly, before stabilizing at a new level. It may be useful to analyze how manufacturers of alternating current electric motors have adjusted prices to these new cost levels.
Do you want to stay up-to-date on commodity market trends?
Sign up for PricePedia newsletter: it's free!
Price Level of Electric Motors
The following table shows the average price levels of 4 types of alternating current (AC) electric motors:
- Single-phase AC Motors > 750 W: these motors are high-power with a single-phase power supply. They are relatively uncommon because they cover specific niche markets;
- Single-phase AC Motors ≤ 750 W: these are medium-power motors with a single-phase power supply. They are important as they are used in household devices such as fans, portable electric tools, and household appliances like refrigerators and washing machines;
- Polyphase AC Motors > 750 W and ≤ 7.5 kW: these motors are high-power and powered by more than one phase of power supply. They are commonly used in electric machines;
- Polyphase AC Motors ≤ 750 W: these are medium-power motors powered by more than one phase of power supply, usually three (three-phase motors). They find extensive applications in industrial contexts.
Price Level (euro/tonn.) of Alternating Current Electric Motors
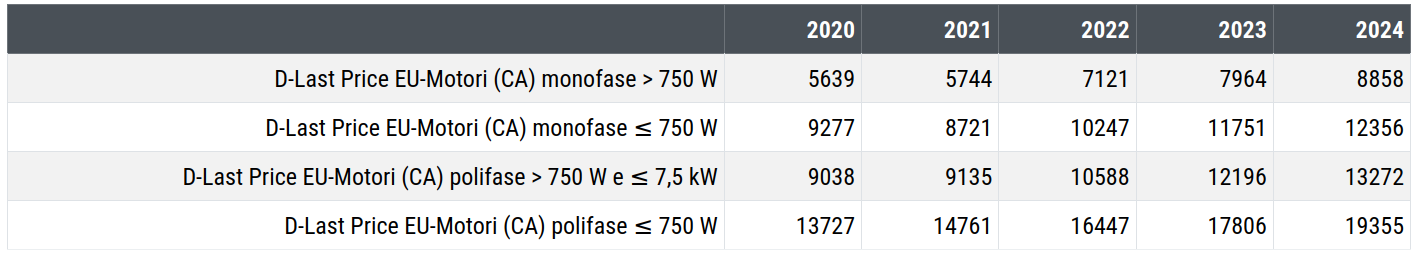
From the analysis of this table, indications consistent with the four types of motors and their respective markets are obtained. Lower prices are recorded for high-power single-phase motors. Prices are expressed in euros per tonne, so it is reasonable that as the size of the motors increases, the costs per unit weight decrease due to economies of scale. The highest prices (per unit weight) are recorded for medium-power polyphase motors. In this case, economies of scale work in the opposite direction. Their higher efficiency and power compared to single-phase motors allow them to maintain a positive differential compared to single-phase motor prices. Within these two ranges are medium-power single-phase motors and high-power polyphase motors, in line with the low economies of scale of the former and the strong market growth of the latter.
Price Dynamics of Electric Motors
Finally, this last table shows the annual price change rates of different electric motors.
For comparison, the dynamics of costs calculated through the previously described should cost are also included. The variation rates are reported based on 2019. In this way, it is possible to verify the speed and intensity of price adjustments of motors relative to changes in their costs.
Price Level (euro/tonn.) of Alternating Current Electric Motors

The information obtained from this table seems sufficiently clear. With the exception of medium-power polyphase motors, electric motor prices adjusted slowly. The adjustment continued in 2023 and 2024, ultimately resulting in an increase in average prices of alternating current electric motors reaching a level about 10% higher than cost dynamics.
Conclusions
The analysis contained in this article highlights the usefulness of customs price analysis even for goods with a high degree of differentiation, as measured by price dispersion. Despite the high dispersion, the joint analysis of multiple prices and a should cost, even simplified, allows the different mechanisms governing markets to emerge and acquire skills that may be useful in negotiation phases.


