The importance of antimony and the supply risk for the European Union
The absence of a European antimony industry exposes the EU to international supply from China
Published by Luca Sazzini. .
Non Ferrous Metals Critical raw materialsAntimony is a semi-lustrous, silver-gray metal that reacts with oxygen when heated to form antimony trioxide, a chemical compound widely used as a flame retardant in plastics, rubbers, paints, and textiles.
The use of antimony as a flame retardant accounts for about 43% of global antimony consumption, with other major uses in modern industry including:
- for the production of lead-acid batteries (32% of global consumption): the addition of antimony improves tensile strength and charging characteristics, reducing unwanted hydrogen production during charging;
- lead alloys (14% of global consumption): used in the production of bearings in the automotive sector and in household and decorative items;
- catalyst for the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) (6% of global consumption);
- in the production of high-quality clear glass (5%): antimony is used as a degassing agent to remove trapped air bubbles in the glass during the cooling phase.
The European Union has recognized the strategic importance of antimony and included it in the list of Critical Raw Materials1 due to its high supply risk. The EU is highly dependent on antimony ore exports from Turkey, which alone represents the majority of European antimony ore imports. More importantly, it is heavily dependent on China for imports of antimony oxide and metallic antimony.
Major Antimony Exporters
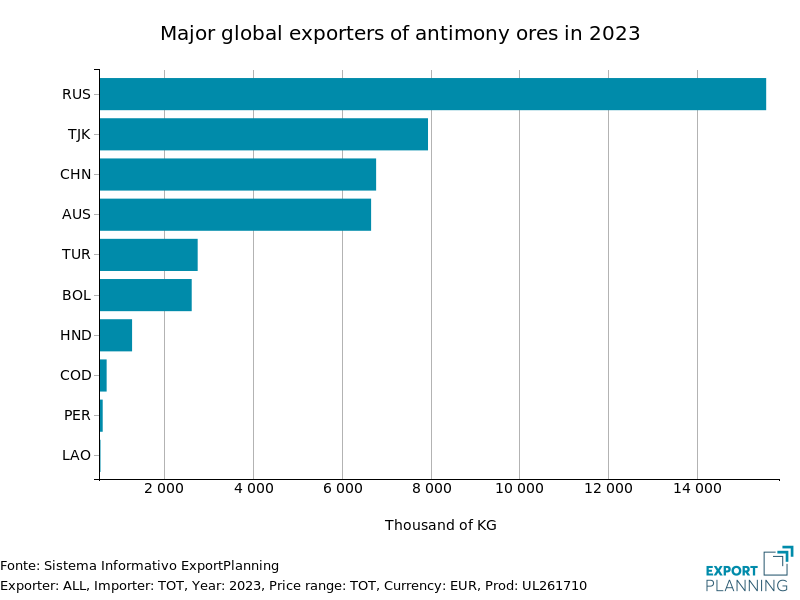
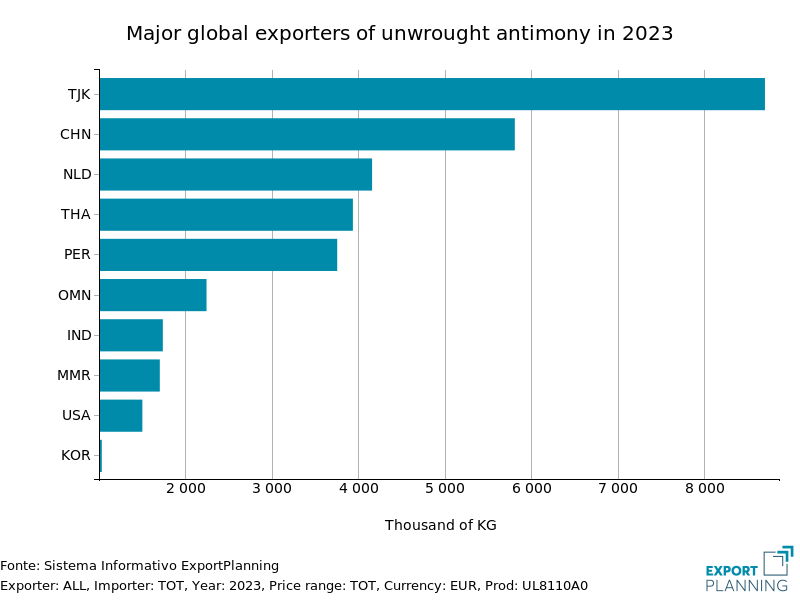
The table below shows two horizontal bar charts indicating the main global exporters of antimony ores and unwrought antimony in 2023.
| Major global exporters of antimony ores in 2023 | Major global exporters of unwrought antimony in 2023 |
|
|
The analysis of the horizontal bar charts shows that in 2023, the largest exporter of antimony was Russia, followed by Tajikistan and China.
China, which used to account for more than half of the world's antimony production, has reduced its extraction capacity due to mine depletion and stricter environmental regulations, leading to the closure of illegal mines that do not comply with environmental standards. Russia and Tajikistan, on the other hand, have expanded their production capacity in recent years and are currently considered the main exporters of antimony ores.
China is expected to continue being the main supplier for future antimony ore supply, although it has currently voluntarily reduced its exports to avoid depletion of its national stocks.
Regarding unwrought antimony, the main global exporters are Tajikistan and China. The Netherlands also records high exports, mainly re-exports of material previously imported from China.
Turkey, the EU's main trading partner for antimony ore imports, is not among the world's major exporters. The European Union could therefore seek to further diversify its imports to mitigate supply risk stemming from the concentration of imports from a single third country.
Analysis of Antimony Customs Prices
In the EU customs market, antimony is traded in the form of: unwrought antimony, antimony ores, and antimony oxides.
The following table shows the average annual customs prices in the European market for each type of antimony traded in the EU.
Table of average annual European customs prices for antimony
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-Last Price EU-Antimony ores | 4790 | 3093 | 5958 | 7498 | 6491 | 7407 |
| D-Last Price EU-Antimony oxides | 6082 | 5180 | 7722 | 10923 | 10188 | 10095 |
| D-Last Price EU-Powders of unwrought antimony | 6002 | 4955 | 8783 | 12396 | 10892 | 11059 |
European customs prices for antimony are very similar to each other, except for antimony ores, which are cheaper due to requiring more processing.
From 2019 to 2020, there was a general decline in antimony prices, followed by a strong growth phase in 2021-2022. In 2023, antimony prices experienced a slight decline before rising again in the early months of 2024, except for antimony oxide, which remained constant. Currently, the prices of unwrought antimony and antimony oxides are 11 thousand and 10 thousand euros/ton, while that of antimony ores is 7,400 euros/ton.
To verify whether the antimony market is a global or regional market, the various prices of antimony oxides in the main world areas can be compared.
The following chart shows the historical series of Chinese export prices for antimony oxides, compared with EU customs prices and US import prices, to see how the former influences the others.
Historical series of customs prices for antimony oxides
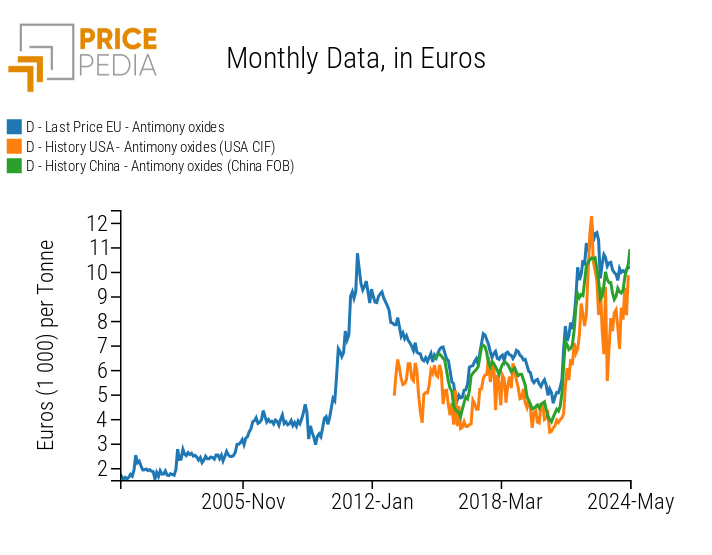
The analysis of the three historical series reveals a strong correlation between the various customs prices of antimony oxides, suggesting the presence of a single global market characterized by strong price contamination, in which China plays a leading role.
Conclusions
The increase in safety regulations will lead to a rise in global demand for antimony as a flame retardant used for fire prevention.
The main global exporters of antimony ores are Russia, Tajikistan, and China. China, although it has significantly reduced its antimony production in recent years, is likely to remain the main supplier for future supply, which is currently expected to decline. With expectations of demand growth and supply reduction, potential market crisis situations on the supply side are logical.
The European Union is a net importer of antimony, dependent on ore exports from Turkey and Chinese exports for antimony oxides and metallic antimony. To mitigate supply risks, the EU is investing in recycling and recovering antimony from secondary materials and planning to diversify its imports to limit possible future supply shortages of the metal.
[1] For further information on Critical Raw Materials, please refer to the article: "Critical Raw Materials: the importance of substitutes"


