Development of the paper recycling sector and new information needs
A case study: price forecasts in Italy for wastepaper
Published by Team Business Market Monitoring A2A. .
Wood and Paper Management
Waste management, from being a cost source, is increasingly becoming a source of economic development, thanks to the growth of supply chains capable of effectively managing all stages of the recycling process, from the initial collection to the final stage of introducing recycled raw materials into the market.
One of the sectors that can be considered mature in terms of process organization is paper recycling. In Italy, 70% of the paper consumed is recycled every year (with peaks exceeding 90% in the case of paper and cardboard packaging) and reintroduced into the production process, greatly benefiting the environment.
The confirmation of the growing importance of the paper recycling economy is evidenced by the formation of a large market, with increasing volumes due to the rise in separate waste collection, increasingly volatile prices, and more significant market dynamics. These factors are accompanied by an increase in various corporate aggregation and M&A activities.
The global size of this market has also grown and thus has the resulting correlation between prices at an international level.
In terms of absorption capacity, Europe has an excess supply of used paper, which fuels an export flow, particularly towards Asian countries.
As competition grows, so does the need to support decision-making processes with accurate and, ideally, predictive information.
Company Needs
A2A is looking with increasing attention at the business linked to paper recycling, given its growing profitability. However, as shown in the graph below, wastepaper prices are highly variable (even compared to other paper prices), making it difficult to predict the dynamics of this business.
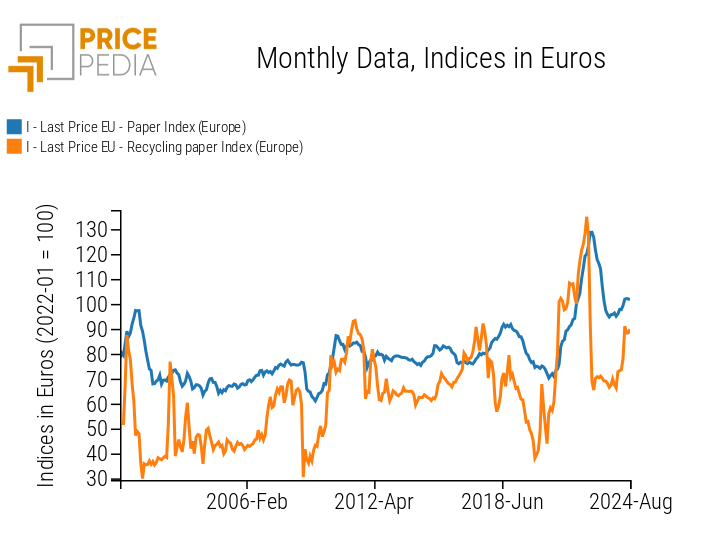
In this context, having access to forecast scenarios and a model that can synthesize the key drivers and their relative importance in price formation can be a useful management tool. This led to the decision to study a model for a 24-month forecast of wastepaper prices, which can be updated periodically. To meet this need we were supported by the PricePedia platform.
The PricePedia Platform
In order to estimate and manage an econometric forecasting model, the PricePedia platform was used. It was developed by StudiaBo S.r.l. as a tool for those working in procurement and sourcing. PricePedia collects daily quoted prices from financial markets and tracks monthly customs price trends for over 500 raw materials and semi-finished products. It also provides a range of tools (reports, composite indices, and forecasting models).
The PricePedia platform allows users to forecast not only the variables already present in the platform but also external variables uploaded by the user. A series of options for model construction and related diagnostics is available. Additionally, there is a reliable and effective support service. However, there are certain flexibility limits that prevent incorporating all the assumptions formulated during the model-building phase and the variables considered (for example, external exogenous variables other than those provided by the platform cannot be inserted, or more complex models cannot be used).
The Wastepaper Price to be Forecasted
The Waste Business Unit, our internal client, identified the market price they are interested in as the wastepaper price in Italy, provided by EUWID, a German company that interviews suppliers, converters, and packaging users every month to collect reliable data on paper prices.
The ability to upload series from other sources into the PricePedia platform allowed us to meet our user's request, developing a specific model and forecasting scenarios tailored to their specific requirements.
The Developed Model
Meetings with colleagues from the Waste Business Unit were held to identify relevant variables for the model development. Additional information sources (Bloomberg, EUWID, Chamber of Commerce, ISTAT) were considered. As the dependent variable, we selected the EUWID wastepaper price series (mixed paper), as previously mentioned.
In addition to the dependent variable, several hypotheses were put forward during the analysis.
However, not all hypotheses were developed in the model due to the
limitations of integrating external information into the platform's set of available exogenous variables.
The selected exogenous variables were as follows:
- recycled kraft paper price, European market (source: PricePedia);
- dummy variables (binary 0,1) starting from January 2018 to capture the effects on the recycled paper market caused by the Chinese government's ban on wastepaper imports;
- dummy variables, starting from January 2020, to account for the effects on the domestic market of Italy's end-of-waste legislation, which regulates the cessation of waste status for paper and cardboard, enabling greater recovery and reuse of collected wastepaper.
The estimation period starts in January 2013, with a two-year forecasting horizon. The dynamic specification of the model is Engle & Granger.
Conclusions
The obtained estimate shows a good fit with the endogenous variable (the R2 index, which measures how well a regression line approximates the real data by reflecting the explained variance relative to the total variance, is very high at 0.901). The sign and value of the coefficients were close to expectations. In particular, the coefficient for the recycled kraft paper price was 1.8, corresponding to the elasticity of the wastepaper price to variations in the kraft paper price. The coefficients of the two dummy variables were as follows: the first was negative, reflecting the effect of reduced international demand due to China's ban on recycled paper imports; the second was positive, consistent with the effect of increased demand in Italy.
The use of the model has proven to be easy,
allowing us to update the forecast for wastepaper prices easily every time PricePedia updates its scenario.


