PricePedia Scenario for November 2024
What effects will the American elections have on commodity prices in the next two years?
Published by Pasquale Marzano. .
Forecast Forecast
The PricePedia Scenario has been updated with information available as of November 7, 2024. The American elections declared the Republican candidate Donald Trump as the winner. The impact of this outcome on the financial commodity markets during the election week is discussed in the article Trump effect on financial markets. However, the impact on physical markets cannot currently be quantified.
Among the measures announced in the president-elect's campaign is a 60% increase in tariffs on China and a 10% increase on "friendly" trade partners to support the American economy. Since the actual implementation of these protectionist measures, as announced, would be difficult, the PricePedia Scenario does not incorporate a U.S. tariff increase of the scale announced in the campaign. A significant increase in U.S. tariffs would weaken, all else equal, the prices of commodities affected by the tariffs, due to a reduction in U.S. demand and an increase in supply in the rest of the world.
The information currently available therefore only indicates an increase in downside price risk in the PricePedia scenario.
Regarding global demand for commodities, the weakness phase continues. In terms of global industrial production dynamics, representing demand for industrial raw materials, this results in a relatively low growth rate in 2024 of +1.2% compared to 2023. In 2025, the index is expected to show higher growth (+2.2%). Starting in 2025, the effects of the current phase of easing restrictive monetary policies by central banks will become more apparent, which tends to positively influence commodity demand.
Do you want to stay up-to-date on commodity market trends?
Sign up for PricePedia newsletter: it's free!
The following graph shows the trend of the global industrial cycle index[1], which mirrors the dynamics of global industrial production.
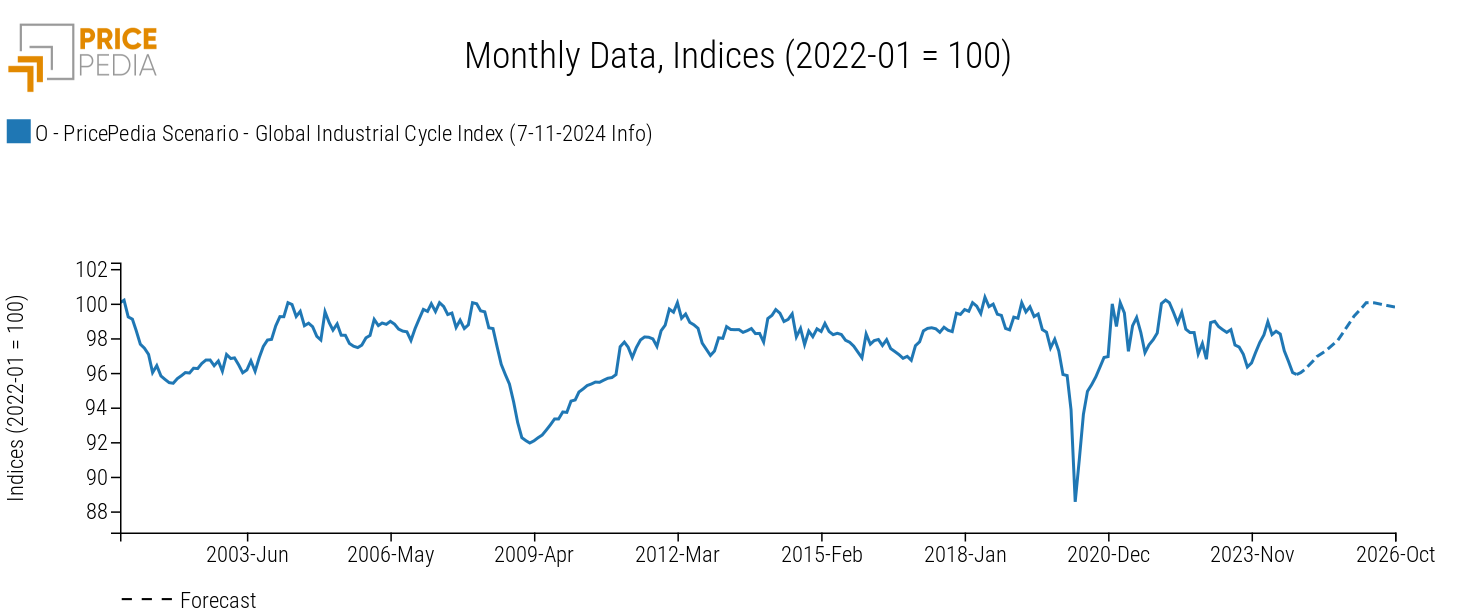
The current weak phase translates into a negative trend in 2024, equal to -0.5% compared to 2023. A change in dynamics is expected mainly in 2025. However, in annual terms, this results in a weakly positive growth rate of +0.4%. More significant growth is expected in annual terms for 2026 with a trend growth of +2.2%.
Price Forecast for purchasing materials
As for the prices of purchasing materials, the trend of the scenario published at the beginning of October is confirmed in aggregate terms.
The table below shows the annual changes in euro prices of the main commodity aggregates (Industrial[2], Commodity[3], and Energy).
| 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-PricePedia Scenario-Commodity Index (Europe) (7-11-2024 Info) | −18.58 | −4.24 | −0.26 | −1.22 |
| I-PricePedia Scenario-Industrials Index (Europe) (7-11-2024 Info) | −14.07 | −3.49 | +5.01 | +0.93 |
| I-PricePedia Scenario-Energy Total Index (Europe) (7-11-2024 Info) | −23.98 | −6.12 | −5.03 | −2.54 |
After the -18.6% decline in 2023, the phase of reduction in euro prices of the Commodity Total continues in 2024 (-4.2%). The downward trend in the index is expected to slow down in 2025 when levels are expected to remain almost unchanged from 2024 (-0.3%). This occurs amid a marked differentiation in the various components of the index: euro prices of energy commodities continue to decrease compared to the previous year (-5%), while euro prices of industrial commodities are expected to recover (+5%) in the same period, in line with the dynamics of the global industrial cycle.
In 2026, the differentiated trend in euro prices for purchase materials is confirmed: industrial prices are expected to increase (+1%), while energy prices are expected to decline by -2.5%.
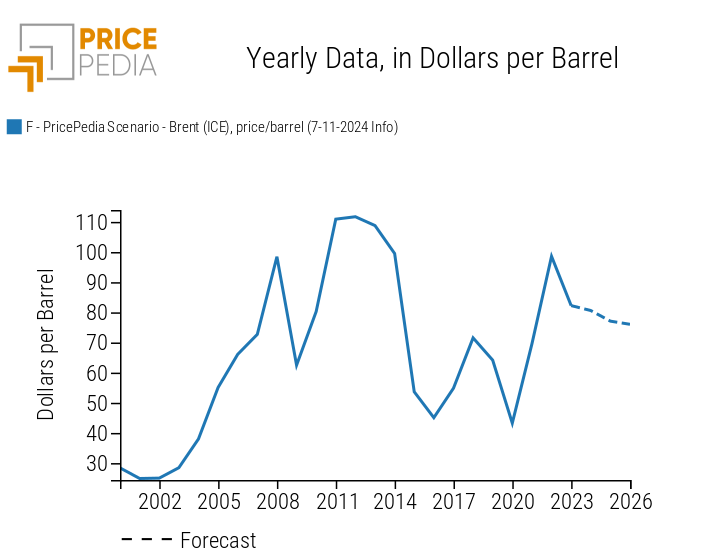
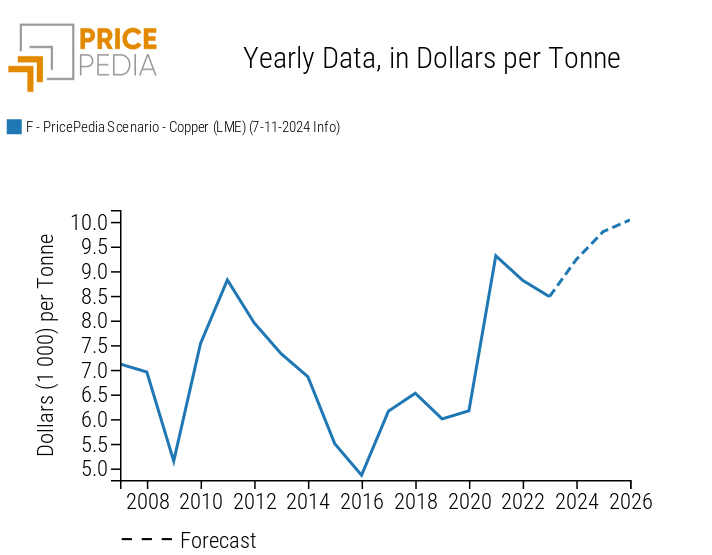
The following graphs show the trends in two representative commodity prices, energy (Brent oil) and industrial (copper), expressed in dollars.
Crude Oil Scenario
Copper Scenario
The dollar price of Brent oil in 2024 is expected to decrease by -2% compared to the 2023 average, stabilizing around 80 dollars per barrel. The reduction is expected to continue in the next two years, reaching an average of about 76 dollars per barrel in 2026.
As for copper, in the first five months of 2024, the price in dollars exceeded the threshold of 10 000 dollars per ton, approaching the monthly high of March 2022. Weak demand, particularly from China, led to a sharp decline in the following months. However, the intensity of the decline was lower than that of the growth phase. Overall, copper prices in 2024 are expected to end up +8.9% higher than the 2023 average. Growth is expected to continue in 2025 and 2026, albeit at a decreasing rate.
Conclusions
The 2024 commodity prices, in euros, are expected to end with a -4% decline, in the context of weak global raw material demand. In the next two years, a gradual recovery is anticipated, supported by easing restrictive monetary policies. However, the currently published scenario highlights an increased risk of further price declines, reflecting uncertainty primarily stemming from the protectionist policies announced by the new U.S. administration.
1. The global industrial cycle index is constructed by purifying the actual dynamics of industrial production from its trend. Since the supply of commodities tends to vary according to long-term economic growth expectations, while the demand for commodities is more linked to actual cyclical uses, the global industrial cycle index tends to reproduce the conditions of tension between demand and supply on the commodity market: when it increases, it means that the demand for commodities increases more than the supply; vice versa when it decreases.
2. The PricePedia Industrials index results from the aggregation of the indices relating to the following product categories: Ferrous, Non-Ferrous, Wood and Paper, Chemicals: Specialty, Organic Chemicals, Inorganic Chemicals, Plastics and Elastomers and Textile Fibres.
3. The PricePedia Commodity index results from the aggregation of the indices relating to industrial, food and energy commodities.


