Price determinants of welded steel tubes
The dynamics of welded steel tube prices depend entirely on the prices of hot-rolled coils
Published by Luca Sazzini. .
Ferrous Metals Steel tubes Long steels Price DriversIn the article: "Update of steel tube prices to December 2024" it was highlighted how the different production process of tubes, based on extrusion or welding of laminates, influences not only the price level of welded steel tubes but also their dynamics, determining significantly different phases for the prices of the two types of tubes. This aspect is particularly evident in the graph below, which compares the price trend of the aggregate index of welded steel tubes with that of unwelded steel tubes.
Comparison of Price Dynamics between Welded and Unwelded Steel Tubes
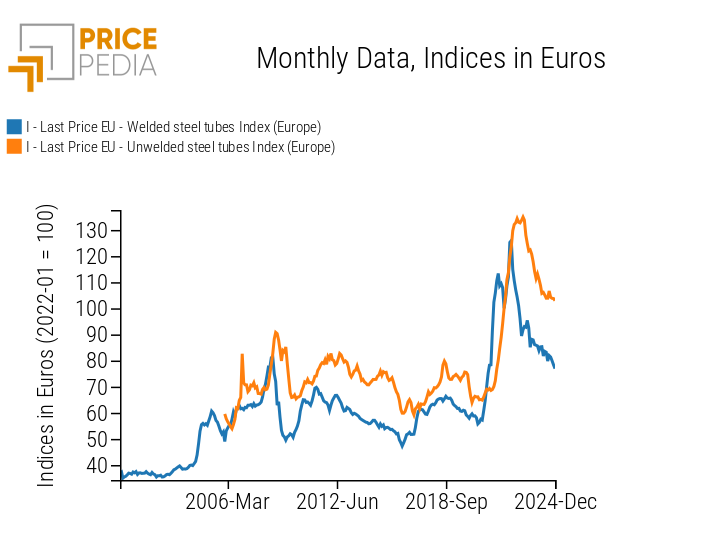
In the latest price cycle, for example, the unwelded steel tube index recorded intense and continuous growth until the end of 2022, followed by a period of stability and a subsequent decline starting in the second half of 2023. In contrast, the welded steel tube index anticipated the growth phase, experiencing an initial decline already towards the end of 2021, followed by a recovery in the first half of 2022, and then a drop in the second half of the year.
These divergences in price dynamics between welded and unwelded tubes highlight the importance of analyzing the two markets separately, avoiding a generic approach that would fail to capture the specific determinants influencing the dynamics of the different types of steel tubes.
This article provides an econometric analysis to estimate the price dynamics of welded steel tubes, while the analysis of unwelded tubes will be covered in a subsequent article.
Econometric Analysis
To estimate the price dynamics of welded steel tubes, it is necessary first to identify the explanatory model, referring to the economic theory on the determinants of commodity prices.[1]
A first study is then conducted on the main variables that, according to economic theory, could have a significant impact on the price dynamics of welded steel tubes.
The first determinant considered is hot-rolled coils, the main production input for welded steel tubes.
In the production process, coils are unrolled, cut to the desired width, and shaped into cylindrical form using a series of rollers, before being welded along the edges to create the finished tube. Their central role in this process makes it plausible to assume a close relationship between the price trends of coils and those of welded steel tubes.
To verify this hypothesis, a graphical comparison is presented between the aggregate price index of welded steel tubes and that of hot-rolled coils.
Comparison between Prices of Welded Steel Tubes and Hot-Rolled Coils
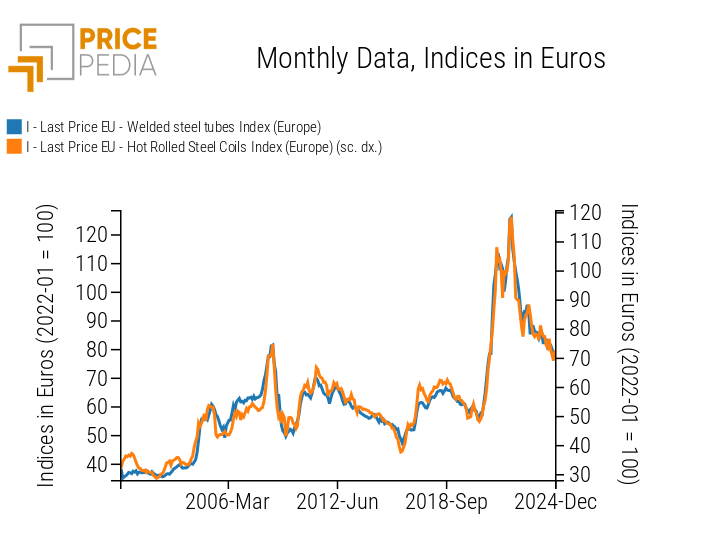
The double-scale graph supports the theoretical hypothesis that hot-rolled coil prices explain and reflect the price trends of welded steel tubes, suggesting the crucial importance of coils within the regression model.
In addition to the raw material costs needed to produce welded steel tubes, labor and service costs used in production must also be considered. To estimate these costs as a whole, the Euro Area Consumer Price Index can be used as a proxy, assuming that wages and service prices are indexed to inflation. This assumption is reasonable since wages tend to follow consumer price trends, thus influencing both labor and service costs.
The third and final variable included in the model is the industrial cycle, used to represent the dynamics and intensity of market demand.
Once the main theoretical determinants of welded steel tube prices are identified, the long-term equation estimation proceeds.
Do you want to stay up-to-date on commodity market trends?
Sign up for PricePedia newsletter: it's free!
Long-Term Estimation
To estimate the long-term relationship, the Engle and Granger econometric model can be used, which allows separating the dynamic specification into two phases.
In the first phase, the long-term relationship is estimated, representing the structural link between the considered variables. If the variables under examination are cointegrated,[2] it is possible to apply the OLS estimator to precisely estimate the long-term equation.
Once the long-term equation is estimated, the short-term dynamics can be estimated by applying an error correction model. This second phase captures the adjustment processes in the short term, showing how the actual values of the variables gradually realign with the "theoretical" long-term values.
Below are the results of the long-term estimation between the prices of welded steel tubes and the main determinants identified by economic theory.
Long-Term Estimation of Welded Steel Tube Prices
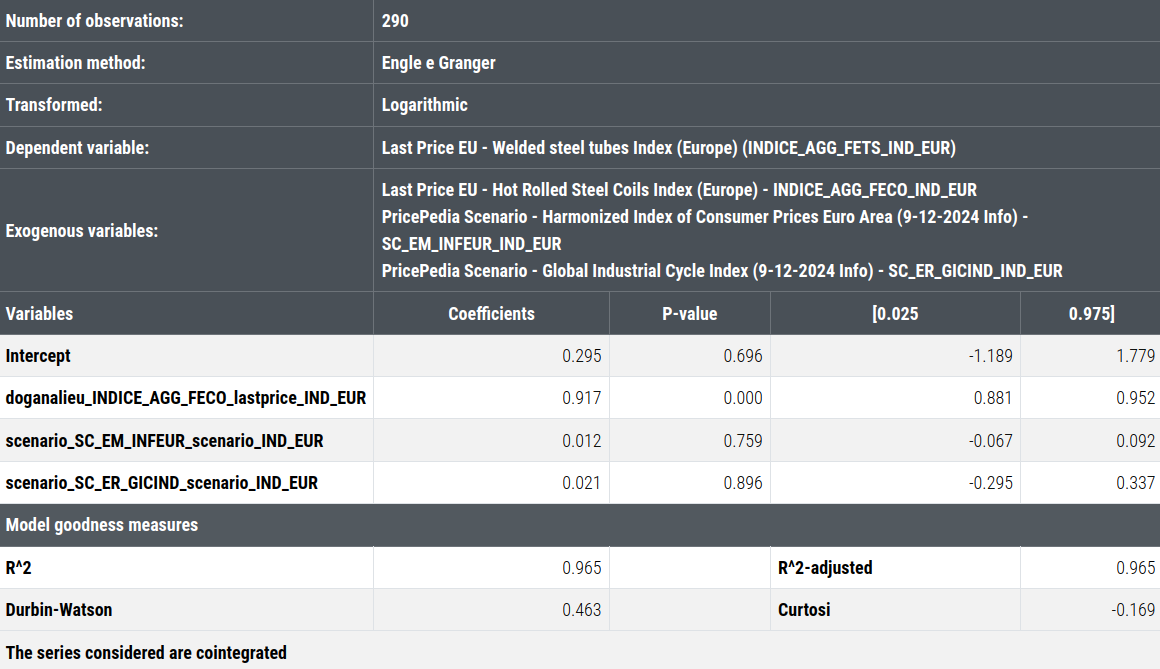
From the long-term regression, it emerges that the price dynamics of welded steel tubes are entirely explained by the prices of hot-rolled coils.
Since the variables are expressed in logarithmic form, the estimated results can be interpreted in terms of elasticity. This means that, ceteris paribus, a 10% increase in hot-rolled coil prices leads, on average, to a 9.2% increase in welded steel tube prices.
The estimated coefficients for the Euro Area Consumer Price Index and the European industrial cycle are both positive, in line with theoretical expectations. However, the values of their coefficients are low, suggesting that the influence of these variables on welded steel tube prices is relatively limited. Statistically, both values are not significantly different from zero.
The R² index, which measures the goodness of the estimated model, is 0.97 out of a maximum of 1, indicating that the model captures 97% of the variability in welded steel tube prices.
Short-Term Estimation
In order to assess the adjustment dynamics of the variables considered, the short-term estimation of the model analyzed above is performed.
Short-Term Estimation of Welded Steel Tube Prices
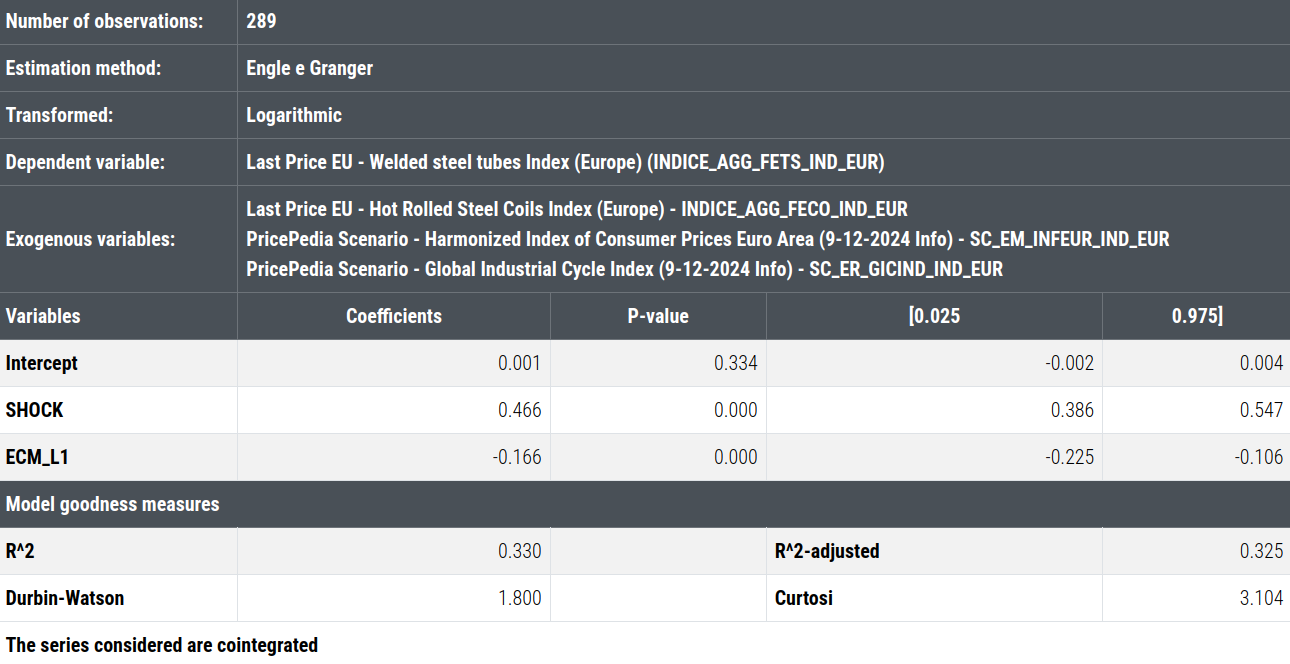
The coefficients of the short-term estimation are all statistically significant.
The coefficient associated with the shock variable (0.47) indicates that almost half of the shocks (47%) due to changes in the determinants are immediately transmitted to the price of welded steel tubes.
The estimated adjustment speed (-0.17) indicates that about 17% of the deviation from the long-term equilibrium is corrected each period.
Conclusions
This analysis highlighted that the price dynamics of welded steel tubes are almost entirely determined by the prices of hot-rolled coils. All else being equal, a 10% increase in hot-rolled coil prices leads, on average, to a 9.2% increase in welded steel tube prices.
The coefficients of the Euro Area Consumer Price Index and the industrial cycle are relatively low, suggesting that their impact on welded steel tube prices is relatively limited.
The short-term results show that 47% of the variations are immediately transmitted to welded steel tube prices. The adjustment speed is estimated at -0.17, indicating that about 17% of the deviation from long-term equilibrium is corrected per period.
[1] A brief description of this theory is provided in the italian article: "Determinanti e previsioni dei prezzi delle commodity";
[2] Two or more variables are considered cointegrated if there exists a linear combination of them that is stationary. In other words, even though the individual variables are non-stationary (i.e., tending to follow an increasing, decreasing, or fluctuating pattern without a stable mean value), their linear combination tends to stabilize around a constant value over time, frequently oscillating around zero.


