Cost Pass-Through in Wood Panels
The transmission of wood price dynamics to panels of different compositions
Published by Pasquale Marzano. .
Wood Engineered wood Cost pass-throughIn recent years, the European wood price has been affected by several shocks: the first in 2021, when strong demand from the U.S. market led to an increase in EU lumber exports, particularly conifers, to the U.S., causing a relative shortage in the EU market; the second following Russia's invasion of Ukraine, which resulted in Europe's halt on imports of wood from Russia and Belarus.
In both cases, the result was an exceptional price increase, as shown in the following graph, which presents the aggregated index of European wood prices.
European Wood Price Index in € (2022-01=100)
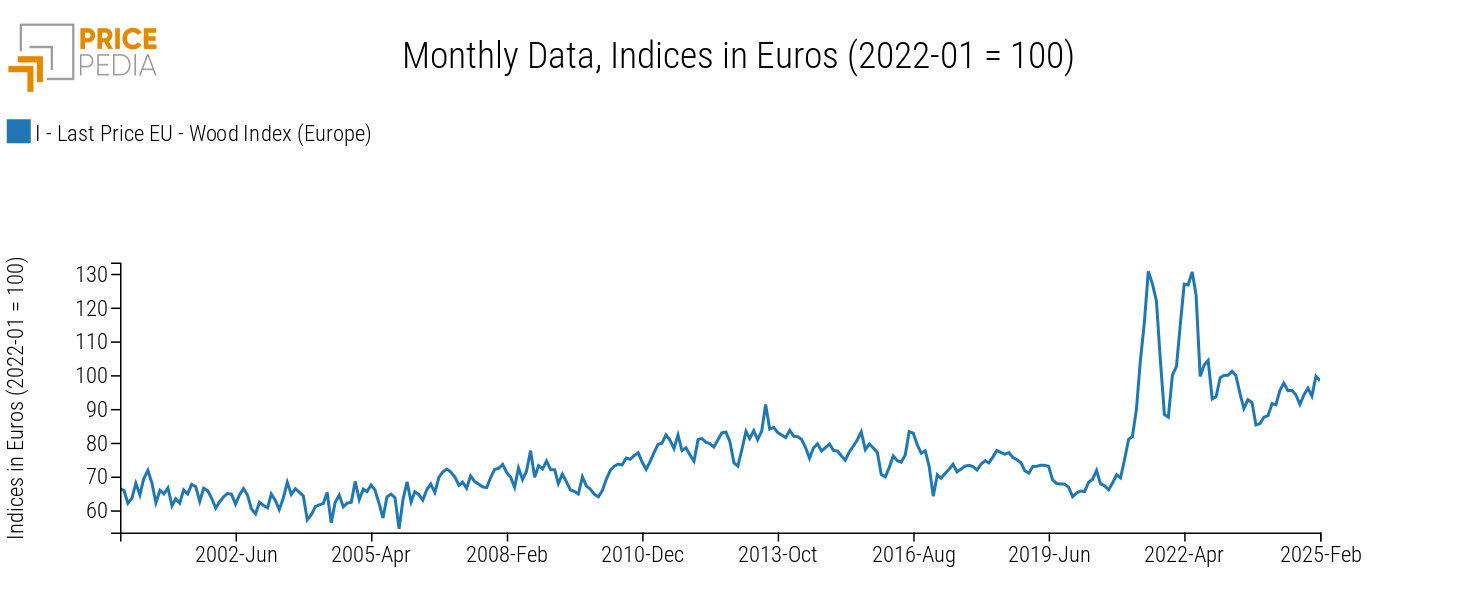
Before 2021, price fluctuations were relatively small. However, starting in 2021, prices spiked significantly, exceeding +84% compared to the long-term average of the previous twenty years.
After a decline in the second half of 2022, prices have remained relatively stable but are still about +32% higher than the 2000-2020 average.
Due to the high product differentiation along the wood supply chain, the above-described dynamics have transferred downstream in a heterogeneous manner.
Below is the reference diagram used by PricePedia to analyze the relationships between products along the wood supply chain.
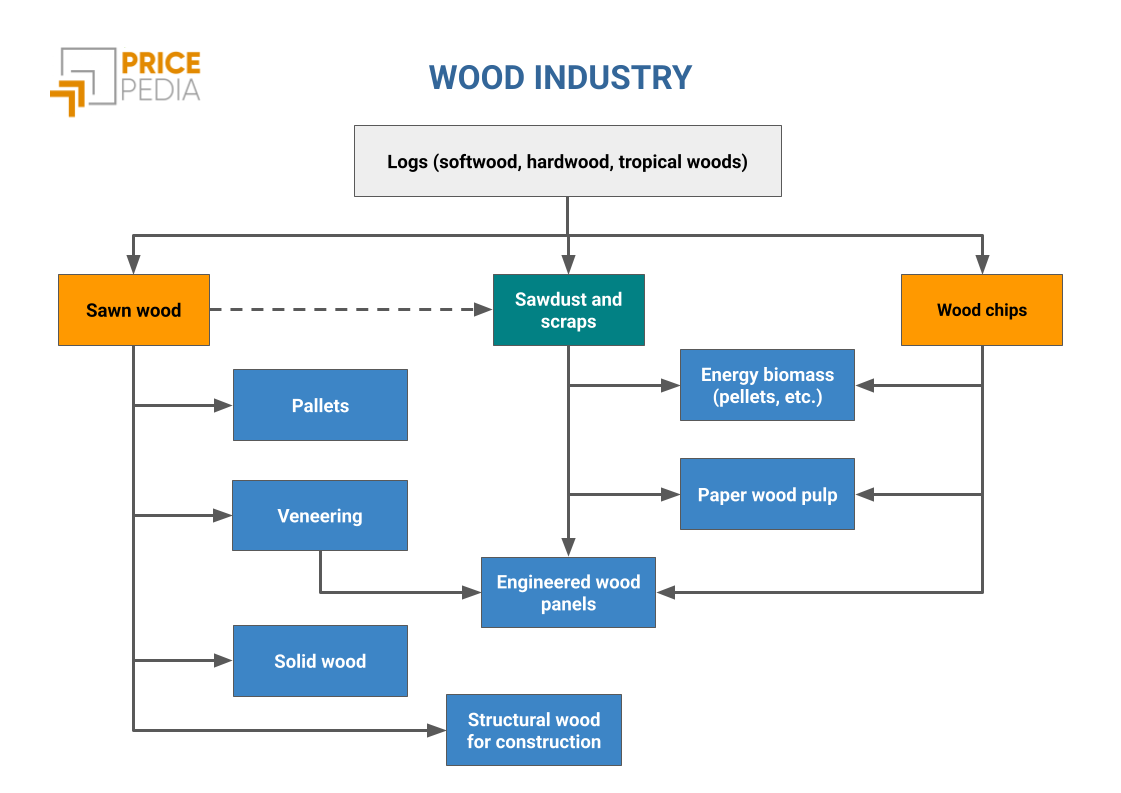
At the upstream of the supply chain are logs, which can come from softwood, hardwood, or tropical woods (which are particularly valuable). The primary processing of logs yields sawn wood, which is used in the manufacturing of:
- pallets,
- solid wood (e.g., for furniture),
- structural wood for construction,
- veneer sheets, used in engineered wood panels.
Vuoi restare aggiornato sull’andamento dei mercati delle commodity?
Iscriviti gratuitamente alla newsletter PricePedia!
The diagram also highlights the efficiency of the wood supply chain, where waste materials are reused, minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact. Processing residues, as well as wood chips[1], are used in the production of both energy biomass and paper, as well as in the production of engineered wood panels, which are considered a sustainable alternative to solid wood.
The case of engineered wood panels
In the article "Russia effect" on wooden panels, the characteristics of some panels such as OSB (oriented strand board) and MDF (medium-density fiberboard) were described: the former is made from layers of wood strands arranged in a specific orientation and is used in construction and packaging; the latter is produced from wood fibers and is considered a substitute for solid wood in furniture production, thanks to the application of veneer sheets in subsequent processes.
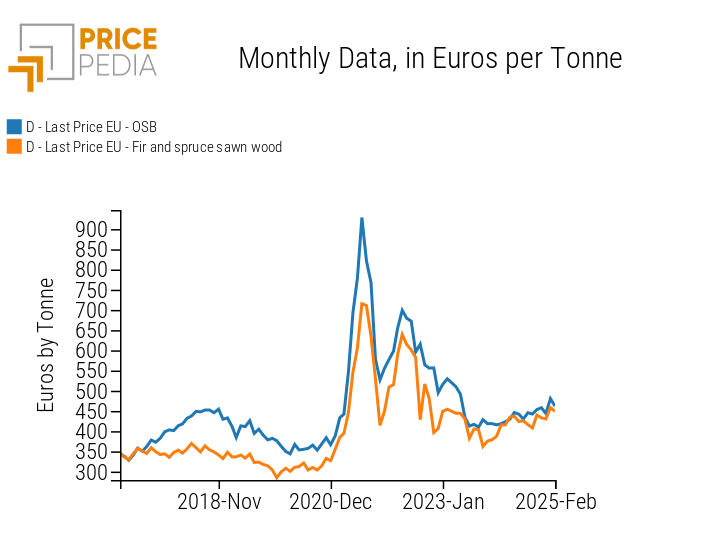
The graphs below compare the prices of OSB and MDF panels with the price of softwood sawn wood.
Prices of Wood Panels and Fir and Spruce Sawn Wood, in € per Ton
OSB Panels
MDF Panels

The left-hand graph shows a common price trend between fir and spruce sawn wood and OSB panels, highlighting a high cost pass-through from raw material to the semi-finished product.
In the case of MDF panels, however, price adjustments occur more gradually, with a less immediate cost pass-through than observed in OSB panels.
This is consistent with the use of other raw materials in MDF panel production, such as a mix of different types of wood and adhesives, as well as their use in highly differentiated sectors such as furniture manufacturing.
1. Wood chips are obtained by chipping logs, branches, sawmill waste, or forest residues.


